Capsim Core Simulation Strategy
Capsim Core Simulation Company’s marketing strategy is focused on positioning in size performance, setting sales and promotional budgets that raises customer’s awareness and accessibility. With a high-quality product, high-tech customers have been willing to purchase our product. Of which, if we can set prices that are attractive to both high and low-tech customers, we will be able to gain a very large position in the market. Our goal is to increase production and offer clients products that are new, advanced, reliable and build high levels of awareness. The company closely monitors the results by tracking profits, people that are involved and competitor’s progress.
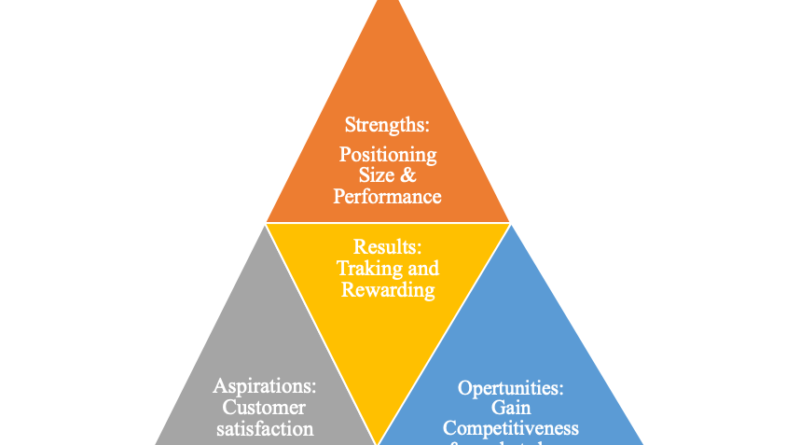
S.O.A.R. Analysis:
SOAR analysis was conducted to show the company’s core competencies, which are the resources that distinguishes Capsim Core’s products and services from the competitor’s products and services: Capsim Core computer sensors are high positioning performers, compact sized, with very high reliability. A SOAR analysis is a strategic planning tool used to focus on a company’s strengths, opportunities, aspirations, results (SOAR) analysis shows the organization’s current strengths and vision of the future for developing its strategic goals (“SOAR analysis,” 2016).
Analysis results:
- Key areas of focus: High quality performance: Awareness & Accessibility: Gain market share: Customer satisfaction, through awareness & reliability: Tracking results and rewarding.
To gain competitive advantage, the company offers a great product that is powerful enough to withhold its effectiveness for both computers and cellphones, but conveniently small enough to satisfy the needs of our customers. The prices of the sensors are competitive for both high-tech and low-tech customers, and the performance of the sensors are higher than most competitors.
S.W.O.T. Analysis:
“SWOT is a method based on internal and external environment of the
organization analysis or a procedural or structural components analysis thereof
embodied in establishing the main strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the organization” (VERBONCU & CONDURACHE, 2016, p. 118).
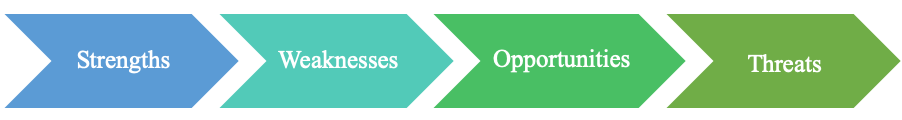
- Internal Strengths:
- Internal Weaknesses:
- External Opportunities:
- External Threats:
The following factors are internal opportunities, internal weaknesses, external opportunities and external threats that influences the global competitiveness of the Capsim Core Company:
- Market efficiency, market size of the company in specific locations, and sources that are needed for the operations, innovation, technological readiness, long-term strategy, capability to adapt to different activities.
- The internal weaknesses of the company that can lead to difficulty when attempting to maintain competitiveness are; financial market development capabilities, unable to operate around the clock to meet demand, and physical location of facilities.
- Market share, versatility, product differentiation and macroeconomic environment.
- External threats are new entry, threats to global environment affecting resources and foreign investments.
GAP Analysis:
“Gap Analysis. It’s a useful technique that enables you to identify the gap between your current situation and the future state that you want to be in, along with the tasks that you need to complete to close this gap” (Manktelow, et. al, (n.d. p.). GAP analysis is used for a organization to increase its performance by getting a clear understanding of where the company’s caps are, then come up with solutions that will closes the gap between the performance and its potential performance.
- Current position:
Capsim Core’s goal is to become one of the world’s largest global computer sensor companies within the next five years, while providing quality sensors to our customers that give them a state of the arts high-performance sensor all within a compact size, offering new products to high segment at a competitive price.
Concentrate more on meeting customer’s criteria and taking things into consideration for the long-term: Increasing customer awareness and better pricing that meets the need of both tech customers: Investing more in automation and capacity: Better budgeting of long-tern debt and limit borrowing money if we are not in need. Focus on placing the company in a better cash position by retaining revenue.
- Vision Statement:
Capsim Core’s vision is to become one of the world’s largest computer sensor companies within the next five years, while providing quality sensors to our customers that gives them a state of the arts high-performance sensor all within a compact size:
- Mission:
- Purpose:
Our purpose is to create a great product that is powerful enough to withhold its effectiveness for both computers and cellphones, but conveniently small enough to satisfy and serve those purposes.
- Philosophy:
We believe that maintaining a relationship internally and externally is an important factor that helps us maximize our success as a company, and with the highest ethical standards, all employees are committed to making the right decision at all times.
S.M.A.R.T. Goals:
“SMART is an acronym for a goal-setting practice, to make sure that goals or objectives are actionable and achievable, at the letters most often stand for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely” (Campbell, 2015, para. 1).
Our main goal is to be one the largest computer sensor chip companies globally by providing quality advanced technology to established businesses so that they can sustain their own competitive advantage with a product system that is reliable and affordable. We are aiming for our product to become more attractive to our customers so that we outsell competitors.
To achieve these goals, the company will invest more in automation that increases performance, reliability and the desired size, position the age and price that is attractive for both high and low-tech customers, increase awareness and accessibility, as we keep a close eye on the market and make adjustments as necessary. The goal is also to invest more into the company’s production so that we are able to produce more by increasing employment and training.
Long-term goals:
Within the next year, the company will have a promotional event that will help increase the business by generating new customers. By a three year mark, our social media network, social events as well as charity events should gain the company recognition while building our brand. So by five years, as a result, Capsim Core Company will be able to increase awareness, boost up revenue while strengthening our relationship with customers. So, by the time our seven year marking period , the company will have already maintained its competitiveness by gaining the interests of our customers through providing them with quality.
Market segment:
Targeting both high-tech and low-tech customers by satisfying high end customers with fast performance and small in size, and low customers with a more slower performance and larger in size. So, the company will position in between both segments.
Competitive advantage:
High investment in training; quality service of employees; high-end performance sensors; reliability; competitive price for both high and low-tech customers; market efficiency; innovation; technological readiness.
Organizational Design:
In order for the company to become successful is to have a great organizational approach to improve the effectiveness of the company. The following design was created to help guide the company through a path that focuses on key points:
Improve efficiency: Provide excellence customer service: Reduction in operational costs: Customer and employee engagement: Clear cut strategic plans to grow the company and increasing profits.
Corporate level goals:
When trying to create large goals, it is best to break them down into individual goals and objectives that are achievable and will lead to the desired destination in the future (GTS, 2013).
Corporate level goals are to increase market share by targeting new customers; innovation, offering new products to the product line; improving employee satisfaction to gain the best performance so that the company can increase its profits. According to Shetty, (1979), “corporate goals are often considered the starting point of effective management, they are the foundation of strategies, plans, priorities, and resource” (Shetty, 1979, p. 71).
Key policies and procedures:
Monitoring the global market for its industry, then identifying any problems that the company may be facing or may face, identify the options available and making improvements as needed. Business process development procedures will be set for managers and employees to follow concerning the objectives and goals of the company, and management will set up training and use competency models to identify weak and strong areas at the operational level.
Conclusion: Principles of the strategic planning process:
It is very important for an organization to make sure that all stakeholders have a clear understanding in what direction the company is currently and headed. What it’s values and missions are, and the purpose of why it exists.
The first thing to consider prior to the process is to understand who the hierarchy level of strategic decision making is. The first step in the process is to address the company’s vision, mission, philosophy, and goals; second step is to translate the company’s strategic posture and planning guidelines; third step formulation of business strategy and broad action programs; fourth step, formulation of functional strategies and broad action programs; six step, consolidation of business and functional strategies at the corporate level; seventh and eighth steps are the definition and evaluation of specific action programs at the business and functional levels; ninth step is the resource allocation or measuring performance; steps ten, eleven, and twelve, strategic and operational budgeting (Arnoldo & Nicolas, 1984).
Arnoldo C., H., & Nicolas S., M. (1984). The Corporate Strategic Planning Process. Interfaces, (1), 47.
Campbell, J. (2015). SMART criteria. Salem Press Encyclopedia,
GTS, L. (2013). Goal Setting: Study Guide, Student Edition. [Place of publication not identified]: GTS Learning, 2013.
Manktelow, et. al, (n.d.). Gap Analysis Reaching Your Ideal Future State. Retrieved from https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/gap-analysis.htm
Shetty, Y. K. (1979). New Look at Corporate Goals. California Management Review, 22(2), 71-79.
VERBONCU, I., & CONDURACHE, A. (2016). Diagnostics vs. SWOT Analysis. Review Of International Comparative Management / Revista De Management Comparat International, 17(2), 114-122.
U. (2016, May 06). Strengths, opportunities, aspirations, results (SOAR) analysis. Retrieved from http://asqservicequality.org/glossary/strengths-opportunities-aspirations-results-soar-analysis/
![]()