The Science of Decision-Making
Decision Quality
There is great importance in learning how to make decisions through the implementation of a process. Decision Quality ensures decisions are benefited from the development and use of a process. This is done using six requirements: setting the right frame, considering alternatives, gathering meaningful data, clarifying values and trade-offs, using logical reasoning, and committing to action (Strategic Decisions Group International, 2017). It is crucial to understand these elements and how they relate to the specific decision being made. By constantly assessing organization factors in reference to these requirements, a leader can identify where in the process there are lacking.
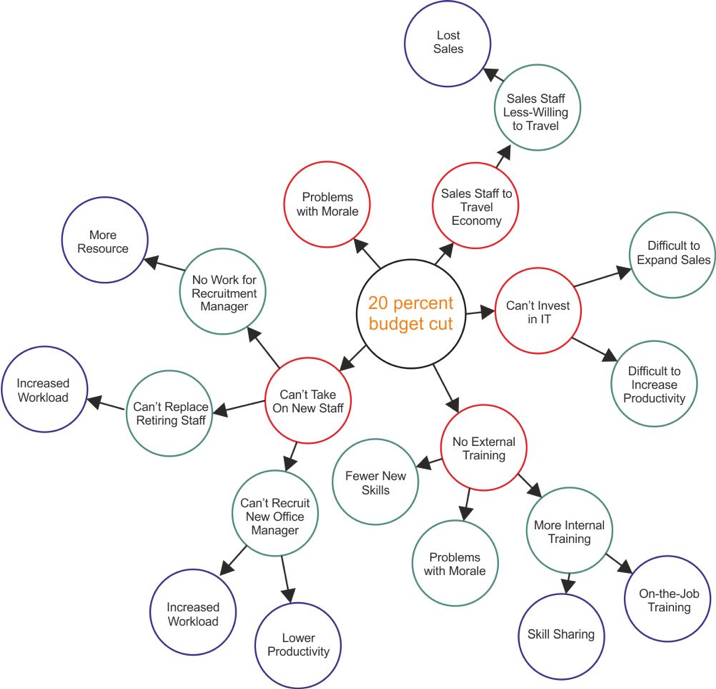
The team at Mind Tools (2017) published information on The Futures Wheel as it emphasizes the need to identify consequences due to change. The page displays a diagram that can be used to map potential consequences of trends or events (Mindtools, 2017):
It is natural to be opposed to change as the risk makes people uncomfortable, but by analyzing each consequence of the change the organization diminish the unknown. It is important to understand these consequences can be both negative and positive. Sharing this will members of the organization can enhance the process of change as they will not be caught off guard by potential negative consequences, and it is likely they will be more “on board” if the positives are identified. The Futures Wheel consists of five steps on how to use the method, including identifying the change; identifying direct, first-order consequences; identifying indirect, second-order consequences; analyzing implications; and identifying actions (Mindtools, 2017).
Personally, I would rather adapt the Decisions Quality as my decision-making strategy. This is because, due to the six requirements, I think Decisions Quality covers a more comprehensive overview of the entire decision-making process while the Futures Wheel focuses on possible outcomes. Though they are both important, I think it is possible to modify the “considering alternatives” aspect of Decision Quality by applying some Futures Wheel practices. Throughout the School Campus, we are currently working to make physical changes to the structure of the University. Top-management placed most faculty and staff within groups assigned to a specific task. The groups have been meeting and discussing various options and will then send their findings back to top-management for final decisions and changes to be made. I think this is an example of where the Decisions Quality would work better than Futures Wheel as it requires data retrieval and analyzation, as well as logical reasoning and commitment. However, I think the Futures Wheel would be more beneficial at the small group level when comparing options. Making decisions is not just understanding the strategies, rather it’s ones ability to know how and when to use each method appropriately and effectively.
References
Mindtools, Ltd. (2017). Decision Tree Analysis. Retrieved from: https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/futures-wheel.htm (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site.
Strategic Decisions Group International, LLC (2017). Decision Quality Defined. Retrieved from: https://www.sdg.com/thought-leadership/decision-quality-defined/ (Links to an external site.)Links to an external site. (Links to an external site.)
![]()

